1. I. INTRODUCTION
he Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is nothing but it is a set of chronic and degenerative disorders that involves alterations in the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, as a consequence of a decreasing in the production of the hormone insulin for the ? cells from the pancreas, and a resistance to the hormone's action in the different tissues [1]. One of the most serious complications of the DM is the DR [2], which is the main cause of worldwide blindness in the economically active population, because it affects people between 20 to 74 years old [3,4]. Two types of clinical DR exist: Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR), also called Background Retinopathy and Proliferative.
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), this work aims to detect the optic disc (OD) and the blood vessels; these are very important & sensitive part from anatomy of eye. Also, the optic disc and the exudates are the bright area of the image. Detection of optic disc and the blood vessels can help the ophthalmologists to detect the diseases earlier and faster. With help of using mathematical morphology methods such as closing, filling, morphological reconstruction and Otsu algorithm Optic disc and the blood vessels can be detected and eliminated.
Main cause of Diabetic Retinopathy is increase in high sugar level in the small blood vessels in retina. This increase in glucose level attacks on tiny blood vassals and optic disk in eye causes increase in ocular Author ?: P D E A's Baburaoji Gholap College, Sangvi, Pune-411057 India. e-mail: [email protected] Author ?: Department of Physics, P D E A's Baburaoji Gholap College, Sangvi, Pune-27. e-mail: [email protected] pressure in eye. Due to increase in pressure vassals may leak, or swelling may be observed in severe stage of retinopathy.
We in this research work using the screening method of diabetic retinopathy which can reduce the risk of blindness by 50% [1]- [2]. Therefore, early detection could reduce the severity of the disease and treating the disease more efficiently. It is very important to detect the optic disc so that after optic disk detection we can identify the other fundus features. The optic disc looks like as the elliptical shape in the eye fundus image. Its size varies from human eye to eye, between one-tenth and one-fifth of the image [3]. In color image, it appears as the bright yellowish region as the exudates. The optic disc is the normal feature of the image but the exudates are the abnormal case. Detection the optic disc can be used to reduce the false positive in the detection of the exudates [4] [5].
A number of methods for optic disc detection and blood vessels detection have been published. Osareh et al. [6] located the optic disc center by means of template matching and extracted its boundary using a snake initialized on a morphologically enhanced region of the optic disc. Lowell et al. [7] also localized the OD by means of template matching as well as also selected a deformable contour model for its segmentation. Another deformable model-based approach was presented in [8]. Another template-matching approach for OD segmentation is the Hausdorff-based template matching presented by Lalonde et al. [9]. Initially, they determined a set of OD candidate regions by means of multi resolution processing through pyramidal decomposition. For each OD region candidate, they calculated a simple confidence value representing the ratio between the mean intensity inside the candidate region and inside its neighborhood. As final step, using the Hausdorff distance between the edge map regions and circular templates with different radii, they decided the OD among all the candidates. There are some methods for blood vessels detection in retinal fundus images such as region growing technique [10] All possible thresholds are evaluated in this way, and the one that maximizes ? is chosen as the optimal threshold. The closing (morphology) operator is useful in detection of vessels. While using closing operator it is important to select structuring element. The closing is a dilation followed by erosion that joins the very close objects together. Then, the result image is binaries by thresholding using Otsu algorithm [16]. The result image is shown in Fig. 6 (b).The filling operator is applied to fill the holes in the image and the result image is shown in Fig. 6 (c). The result image is reconstructed by using the morphology reconstruction and is shown in Fig. 6 (d). To detect the optic disc region, the Otsu algorithm is applied on the difference between the original image and the reconstructed image. The optic disc detected area is shown in Fig. 6 (e). The results of the optic disc detection are shown in Fig. 6
2. III. ALGORITHM FOR OTSU'S METHOD

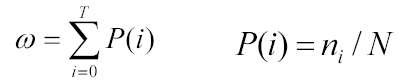
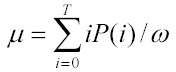
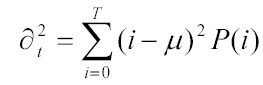
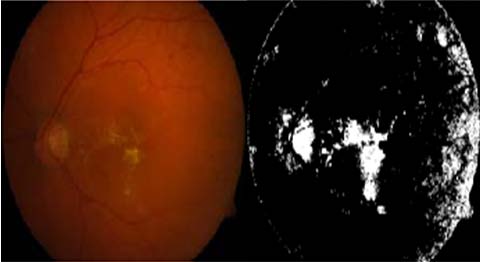
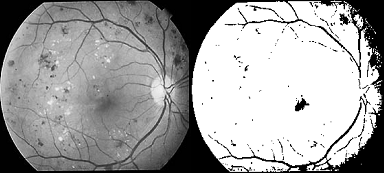
![Fig. 5 : (b) Result of averaging filter VII. Result & Discussion Otsu's method is used to detect damaged optic disk & damaged nerve fibers. For which 1) we compute a mean value of colors with maximum intensity by applying a global threshold to convert an intensity image to a binary image. By normalized intensity value that lies in the range [0, 1]. 2) We have removed a Noise of grayscale image & then applied adaptive wiener filtering & by median filter; by estimating the local mean and variance around each pixel. Thus as shown in figure (1 & 2) only selected damage nerve fibers & optic disk is observed.](https://medicalresearchjournal.org/index.php/GJMR/article/download/100601/version/100601/5-Optic-Disc-and-Blood-Vessels_html/10168/image-8.png)