1. Introduction
astro-intestinal duplications are uncommon anomaly. The incidence has been reported as 1 per 4500 births by the various authors 1 . Due to complications of acute abdomen or bowel obstruction, most cases (65-80%) are detected in children by the age of 2 years 2,3,4,5,6,7.8 . This is the reason that most cases have been reported in children and a few number of cases have been reported in adults. Amongst gastro -intestinal duplication colonic duplication represents only 7 -20% cases 2,3 . Fotiadis et al stated that most of the time definitive diagnosis of colonic duplication is made during a laparotomy 6 .
The differential diagnosis includes enteric cyst, giant colonic diverticulum, volvulus colon, duplication cyst. If not diagnosed in childhood, then these anomalies may come to notice in the later life as a chance finding (being asymptomatic) during an unrelated surgery. When associated with symptoms of intestinal obstruction, volvulus or compression of normal adjacent bowel by the expanding blind end duplication 6,9 . It may also present with symptoms and signs of diverticulitis 10 . Rarely in case of presence of ectopic gastric mucosa with ulceration bleeding or perforation may occur 9,10 . The relative occurrence of digestive duplication has been reported as follows 2,11 .jejunum 8%, Ileal 30%, ileocecal valve 30%, colon 6-7%, rectum 2-3%. The complications of colonic duplication include development of adenocarcinoma, squamous carcinoma and carcinoid tumour 12,13,14 . Fora true digestive duplication, Rowling has set forth the following criteria 15 -1. The wall of duplication should be in continuity with one of the duplicated organs. 2. The cyst is surrounded by a smooth muscle layer.
2. A layer of digestive mucosa is present (Typical or Heterotrophic).
Examples include gastric/colonic/pancreatic II.
3. Case Report
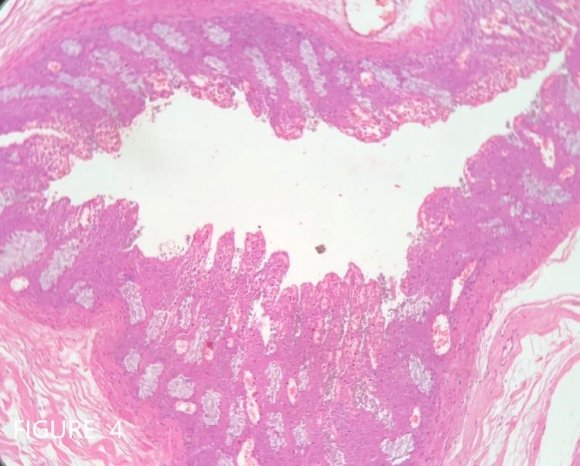
A 45 Year aged male was brought to ER as a case of acute abdomen. He had severe pain in abdomen, abdominal distension and h/o obstipation. He had signs of intestinal perforation. A bed side U/S and Xray abdomen erect (in sitting position) revealed free air under dome of diaphragm and also shadow of colonic lump. The findings were suggestive of intestinal perforation. Patient did not consent for CT abdomen, and hence with a presumptive diagnosis of volvulus sigmoid colon with perforation emergency exploratory laparotomy was done. Exploration revealed a free 40 cm long segment of colon that originated proximal to hepatic flexure. The duplicated ascending colon had a blind end distally, that reached pelvic brim. It was grossly distended and there was a big perforation at its origin from the primary colon (Figure 1, 2 and 3). The ascending colon was excised from proximal to origin of duplication along with right colonic flexure. Both colonic ends were closed and a side-to-side hand sewn anastomosis was done. A covering proximal loop ileostomy was formed for temporary diversion. Patient had postoperative sepsis and had a prolonged hospital stay of 21 days. 4 months later uneventful ileostomy closure was done.
4. Diagnosis and Management
Sonography, CT scan, Contrast enema and Colonoscopy have been suggested for the diagnosis 16 . Contrast CT is best modality in diagnosis, however preoperative diagnosis is difficult 17 . In addition, MRI and Contrast MRI have also been used in the diagnosis of colonic duplication.
Surgical resection of duplication with attached normal colonic segment to avert the risk of developing cancer in the duplicated colon is recommended 2,3 . Currently laparoscopic resection of colon duplication has been advocated 18,19,20 . Laparoscopic surgery is a preferred approach in the management of gastrointestinal duplications 21 . In huge barrel shaped colonic duplication selective mucosal excision with preservation of sero-muscular layer or distal internal drainage by excision of the common wall of duplication may be an effective alternative 2,3,5,22 .
IV.
5. Aetiogenesis, Classification and
Review of Literature Type III Tubular colonic duplication Stern at al reported that 80% colonic duplications are cystic type, and 20% cases are tubular 5 .
Another classification envisages length/extent of involvement of colon/bowel. 2 Types are described -Type I is limited to colon or rectum and is usually partial. If these lesions project into the lumen of bowel, patient may have intussusception leading to obstruction 5,28 . Type II duplications most of the time involve entire colon and are associated with genital or lower urinary tract anomalies. These may also be associated with intestinal mal rotation, duplication of ileum and appendix, spinal anomalies, omphalocele, exstrophy of urinary bladder and other abdominal wall anomalies. Double barrel duplication is usually associated with distal anomalies, terminal fistula or imperforated anus(type IIb and c). These duplications communicate with the bowel proximally, and in most cases do not have distal communication. Thus, these may become distended with faecal matter and cause obstruction of the adjacent bowel 29,30 . Patient may have pain due to over distension or inflammation. Due to ulceration of the aberrant mucosa present in the duplicated segment, gastrointestinal bleeding may occur 4 . Unless associated with another congenital anomaly, duplication having a distal communication are usually asymptomatic. Usually, duplication is present along the ante mesenteric border of bowel, whereas it is lateral in position in case of ascending colon. Transverse colon duplications occur along supra colic margin. Rectal duplications occur posterior to rectum and both have common mesentery and blood supply, however loop duplication have a separate mesentery and blood supply. Tubular duplications sometimes can have direct communication with perineum 3,30 . Tubular type of colonic duplication (T or Y type) have only one communication with the native bowel and the other end forms a blind pouch (as in our present case). Sometimes the distal end may communicate distally forming perianal and Genitourinary fistula and imperforated anus 20 .
Due to number of cases being small, literature has mostly case reports rather than large series or multiinstitutional series. Rarely complete duplication of colon may occur 29,30 . Reporting cases from 1950 -2005, Fotiadis C et al reported total 83 cases 6 .
Roberts M et al reported 2 cases of sigmoid duplication that were pre operatively misdiagnosed as carcinoma 7 . Historically a case of colonic triplication has Historically first case of colonic duplication was reported in 1733 by Cadler 23 . Another case was described by Suppinger in 1876, and the term 'duplication of alimentary tract' was first coined by Ladd in 1937. The exact cause of colonic duplication remains unknown, however environmental factors like trauma and hypoxia etc. have been implicated in its formation 24 . Lewis et al proposed the diverticular theory, whereas alterations in closure of embryonic disc have been attributed as the cause of colonic duplication by others. Yet another theory regarding colonic duplication was proposed by Smith. It describes dorsal protrusion of yolk sac caused by its herniation or adherence to ectoderm responsible for the condition. This theory explains the Genito-urinary problems associated with duplication of hindgut. However, the most plausible theory having comprehensive explanation is given by Bremer. It states aberrant lumen recanalization of the gut in the embryo as the cause of colonic duplication. Since the duplication develops within the intestine, the outer wall contains all tissue layers and its counterparts 25 . been reported by Gray, A.W. 31 Lee KH et al reported laparoscopy for the first time in the management of intestinal duplication in a child 32 . A case of asymptomatic tubular duplication of transverse colon has been reported by Kim YW et al 33 . 2 Cases of colonic duplication that presented as rectal bleeding have also been reported by Fotiadis C et al 6 . 7 case reports of colonic duplication in adults were also reported. Of these 4 patients presented as abdominal pain and 3 had intestinal obstruction 34 . A 'Y' shaped colonic duplication has been reported by Chang et al 35 . A. Sozutek et al reported a case of perforated caecal duplication cyst presenting as peritonitis 36 . An adult female had a sigmoid colon duplication, that was preoperatively diagnosed as colonic diverticula 8 . Jung Hi et al have reported a complete tubular duplication of colon in adult female with Colo-vaginal fistula 37 . Wu X et al also reported a case of tubular colonic duplication in an adult 38 . Another anomaly presenting with multi segmental asymptomatic duplication of colon has been reported 39 . Kung-Chuan Cheng et al reported a case of colonic duplication that presented as a huge abdominal mass in an adult female 40 . Yet another case of colonic duplication cyst in adult female has been reported by Shrestha S and Adhikari S 41 . Li GB et al managed a case of tubular colonic duplication and published it 42 . Recently Reddyn V et al reported a case of intestinal duplication in an elderly male that presented as sigmoid volvulus 43 .
V.
6. Take Home Message
Diagnosis of colonic duplication should be suspected in an adult with chronic colicy pain with constipation as the condition may get unrecognized till adulthood. Patient may also have abdominal lump, distension-usually chronic in nature. However rarely it can also present as acute emergency. The pre-operative diagnosis may be difficult without radiological investigations because of vague clinical and radiological presentation. Treatment is to admit the patient and do open or laparoscopic resection of duplication along with attached normal colonic segment.